
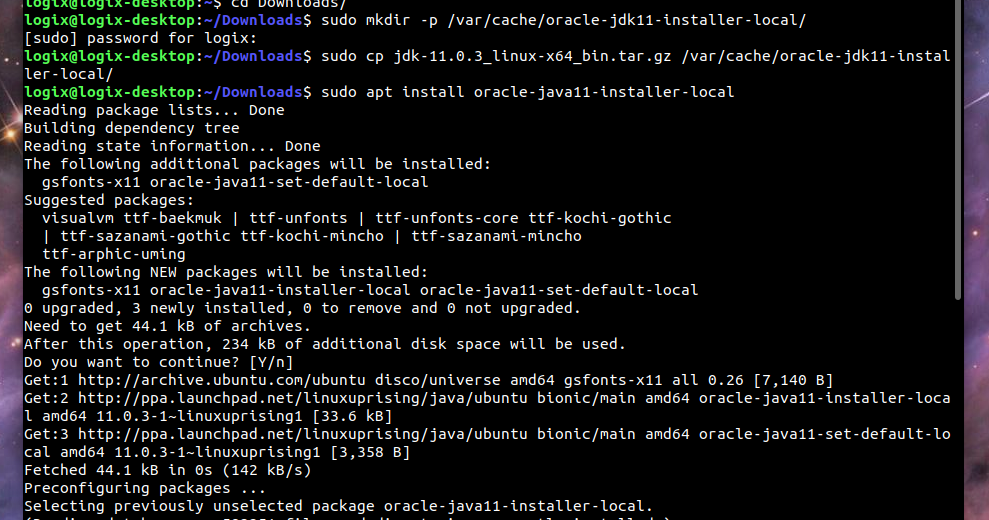
#Java 7 download ubuntu install#
In this article, we will install Tomcat into the /opt/tomcat directory. To proceed with the installation, let’s download the binary distribution file first. You can navigate to for more recent version, if any. When writing this tutorial, the latest stable Tomcat to download is version 9.0.35. OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.7+10-post-Ubuntu-3ubuntu1, mixed mode, sharing) 3. OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.7+10-post-Ubuntu-3ubuntu1) Once installed, we can check the version using this command: # java -version java -version We can install the default JDK, version 11, which is available on the built-in Ubuntu 20.04 repositories by using the following command: # apt install default-jdk -y We need to have Java version 8 or higher installed on your system to run Tomcat 9. If there is no output, it means that Java is not installed on the server yet. We can check if Java is already installed using this command: # which java
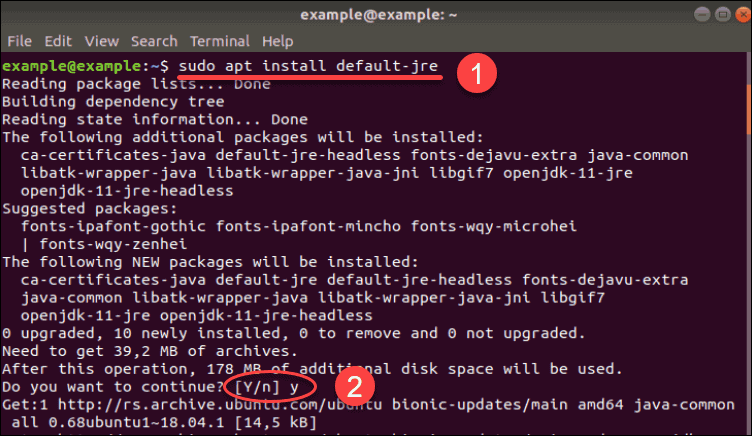
Tomcat 9 requires Java version 8 or higher. Then, run the following command to make sure that all installed packages on the server are updated to the latest available version.

You should get this as your output: Distributor ID: Ubuntu Once logged in, you can check whether you have the proper Ubuntu version installed on your server with the following command: # lsb_release -a Make sure to replace “IP_Address” and “Port_number” with your server’s actual IP address and SSH port number. Log in to your Ubuntu 20.04 VPS using SSH: ssh -p Port_number
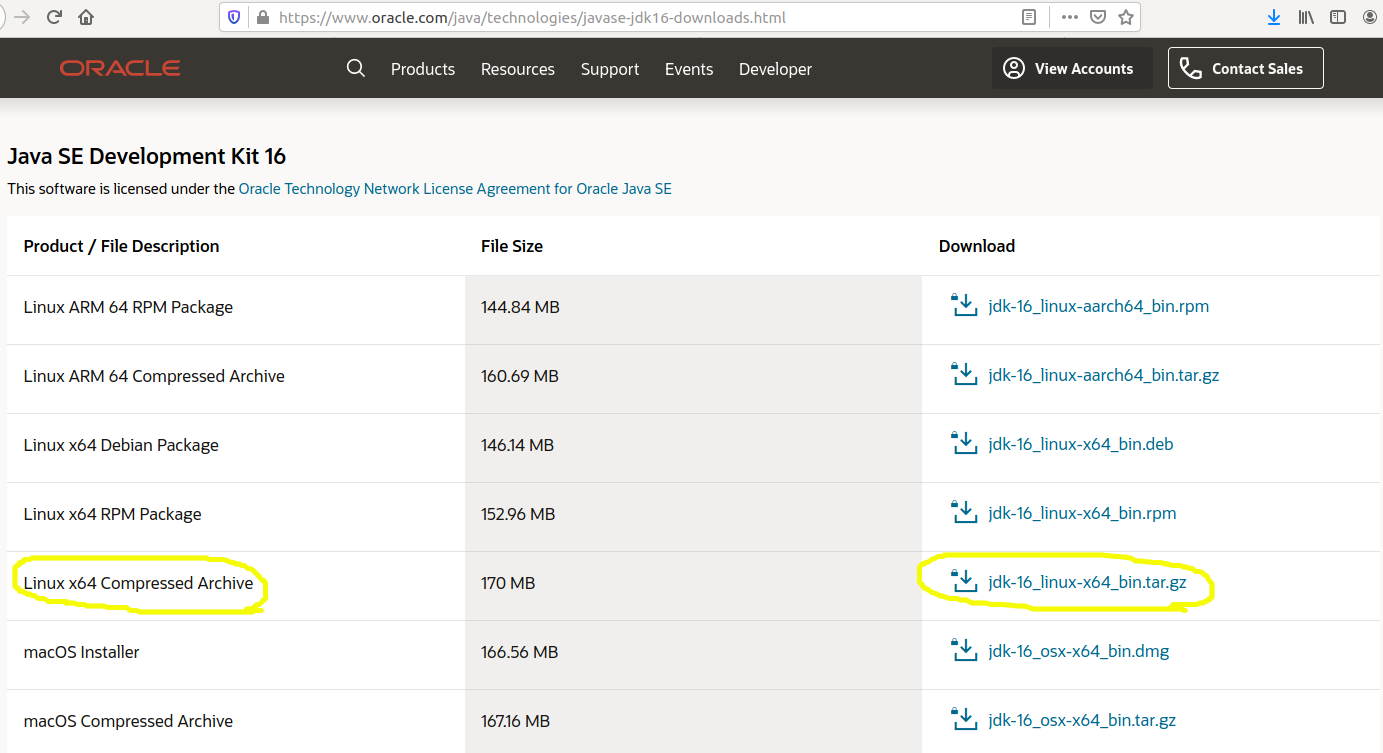
#Java 7 download ubuntu full#
Full SSH root access, or a user with sudo privileges is also required.For the purposes of this tutorial, we will use a server running Ubuntu VPS 20.04 LTS.Make sure that your server meets the following minimum requirements:
#Java 7 download ubuntu code#
Get the code to Launchpad and join our development community. Bugs Handle Bugzilla.time() changes in Bugzilla 5.1.1 (#1774838) Cope with the comment author field being renamed to creator in recent Bugzilla versions (#1774838) Build farm Set the hostname and FQDN of LXD containers to match the host system, though with an IP address pointing to the container (#1747015) Bugs Parse a few more possible Savane URL formats (#197250) Compare Bugzilla versions properly when checking whether they support the Bugzilla API (part of #1802798) Build farm Configure snap proxy settings for Subversion (#1668358) Support passing IMAGE_TARGETS, REPO_SNAPSHOT_STAMP, and COHORT_KEY Here’s a brief changelog of what we’ve been up to since our last general update. Launchpad news, July 2018 – January 2019.Build farm Allow dispatching builds with base images selected based on the pocket and/or using LXD images instead of chroot tarballs where appropriate (#1811677) Code Store bzr-svn‘s cache in the import data store Allow project owners to use the Bazaar branch rescan view Canonicalise expected rule ordering in Bugs Add basic GitLab bug linking (#1603679) Expect the upstream bug ID in the “number” field of GitHub issue objects, not the “id” field (#1824728) Include metadata-only bug changes in Person:+commentedbugs Build farm Filter ASCII NUL characters out of build For example, when somebody adds a comment to a bug, Launchpad sends Launchpad sends a lot of email, most of which is the result of Launchpad users performing some kind of action. The From: addresses used by Launchpad’s bug notifications have changed, to improve the chances of our messages being delivered over modern internet email. Bug emails now use the bug’s address in the From: header.This has generally worked well, but one significant snag became clear later on: it was difficult to add HTTPS support for PPAs due to the way that cookies work on the web. Since they were introduced in 2007, Launchpad’s Personal Package Archives (PPAs) have always been hosted on.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
